Automation Products
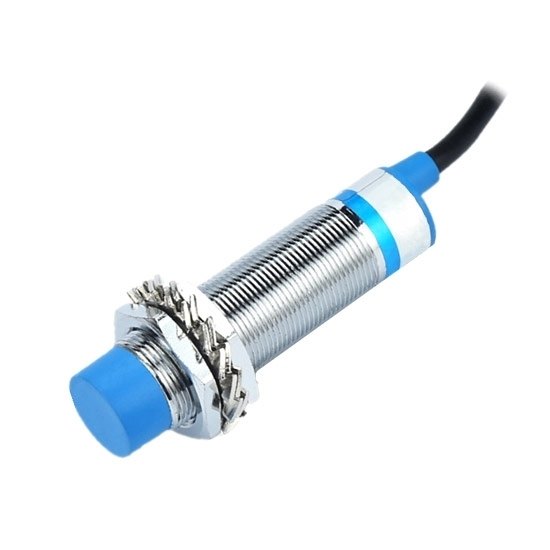
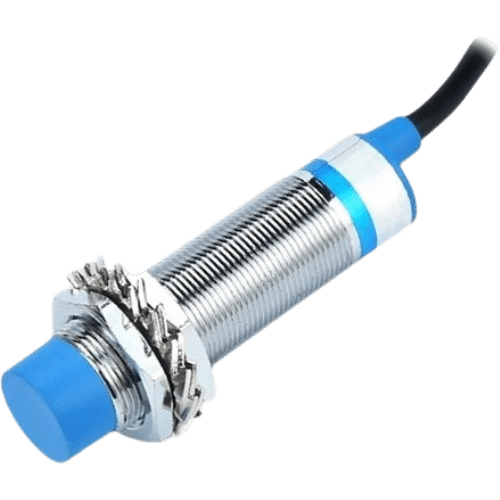


Proximity Sensor
A proximity sensor often emits an electromagnetic field or a beam of electromagnetic radiation (infrared, for instance), and looks for changes in the field or return signal. The object being sensed is often referred to as the proximity sensors target. Different proximity sensor targets demand different sensors.
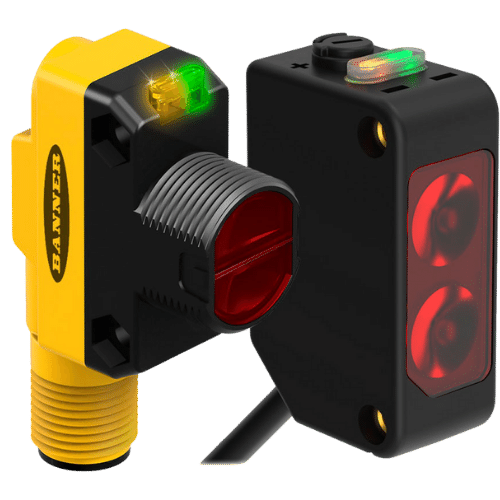

Photo Electric Sensor
A Photoelectric Sensor consists primarily of an Emitter for emitting light and a Receiver for receiving light. When emitted light is interrupted or reflected by the sensing object, it changes the amount of light that arrives at the Receiver. The Receiver detects this change and converts it to an electrical output. The light source for the majority of Photoelectric Sensors is infrared or visible light (generally red, or green/blue for identifying colors).
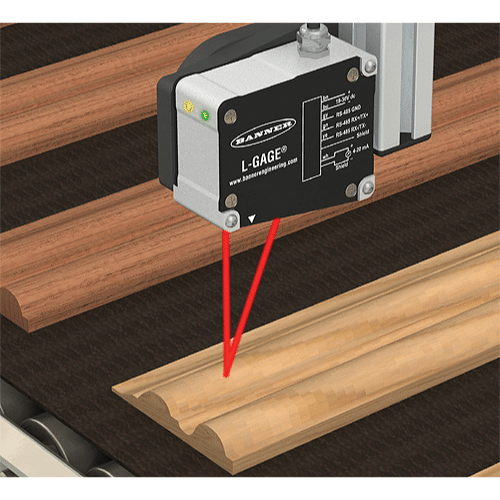
Laser Distance sensor
A laser distance sensor is a non-contact measuring device that uses laser technology to accurately determine the distance between the sensor and an object. It emits a laser beam that reflects off the target and returns to the sensor, which then calculates the distance based on the time it takes for the laser to travel and return. This sensor is commonly used in various applications such as robotics, automation, and construction for measuring distances, heights, and depths with high precision and reliability.
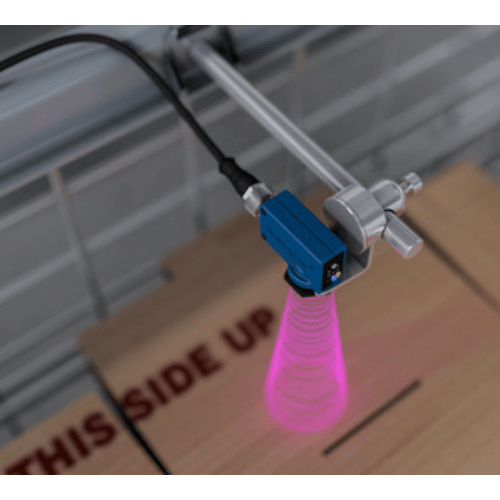
Ultrasonic Sensor
An ultrasonic sensor is a non-contact distance measuring device that utilizes high-frequency sound waves to determine the distance between the sensor and an object. It emits ultrasonic pulses and measures the time it takes for the echoes to return, allowing for precise distance calculations. These sensors are commonly used in various applications such as obstacle detection, object tracking, and distance measurement in robotics and automation. They offer several advantages over traditional contact-based sensors, including non-contact operation, high accuracy, and wide measurement ranges.
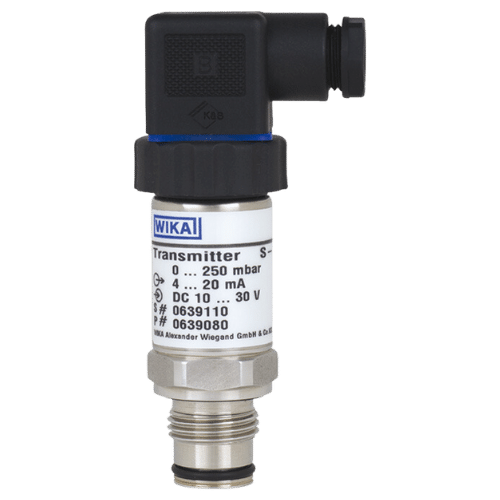

Pressure Sensors
Pressure sensors are essential components in various industries, from automotive and aerospace to medical and environmental applications. These devices measure the force applied per unit area, converting it into an electrical signal that can be read and interpreted by a control system. Pressure sensors come in different types, including piezoresistive, capacitive, and piezoelectric, each with its unique advantages and limitations. The piezoresistive type is the most common due to its high accuracy, stability, and low cost. Capacitive sensors, on the other hand, offer fast response times and high sensitivity but are more expensive. Piezoelectric sensors are less common due to their limited range and sensitivity to temperature and humidity. Regardless of the type, pressure sensors play a critical role in monitoring and controlling processes that involve fluid or gas flow, such as pumping systems, valves, and pipelines. They also enable the detection of leaks or abnormal pressure changes, ensuring safety and preventing equipment damage. In summary, pressure sensors are indispensable tools in various industries that provide accurate and reliable measurements of pressure levels, contributing to efficient operations, enhanced safety, and environmental protection.
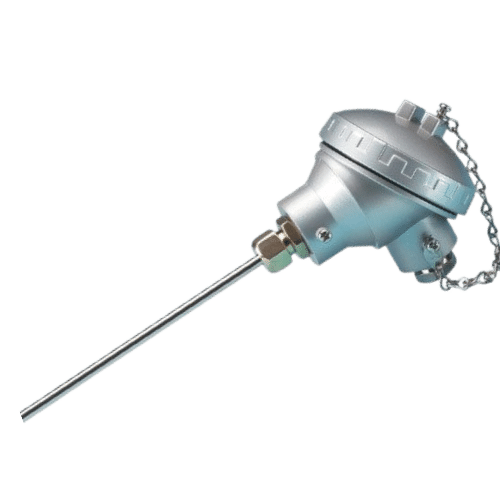

Temperature Sensor
The temperature sensor is a crucial component in various electronic devices as it measures the temperature of the environment and provides feedback to the system. This sensor converts the temperature value into an electrical signal, which can be read and interpreted by a microcontroller or other electronic circuitry. The type of temperature sensor used depends on the specific application, with options including thermistors, thermocouples, and RTDs (resistance temperature detectors). Accuracy, response time, and operating range are key factors to consider when selecting a temperature sensor for a particular application.
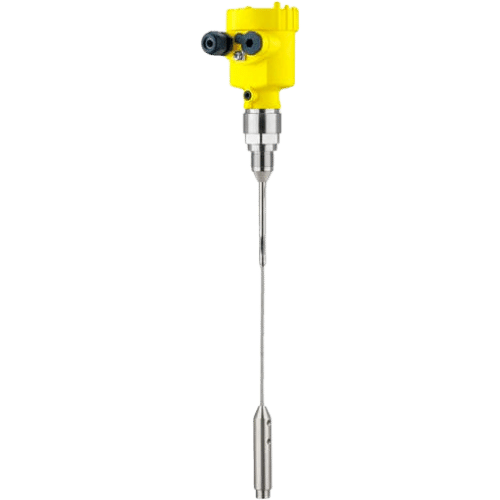

Level Sensors
Level sensors are devices used to measure the height or volume of liquids or solids in tanks, vessels, or containers. They are essential in various industries such as chemical processing, food and beverage manufacturing, and water treatment to monitor the level of fluids accurately and efficiently. These sensors can provide real-time data on the level of the material, enabling operators to optimize production processes, prevent overflows or underflows, and ensure safety by detecting low or high levels. Level sensors come in different types, including float switches, ultrasonic sensors, radar sensors, and capacitive sensors, each with its own advantages and limitations depending on the application.
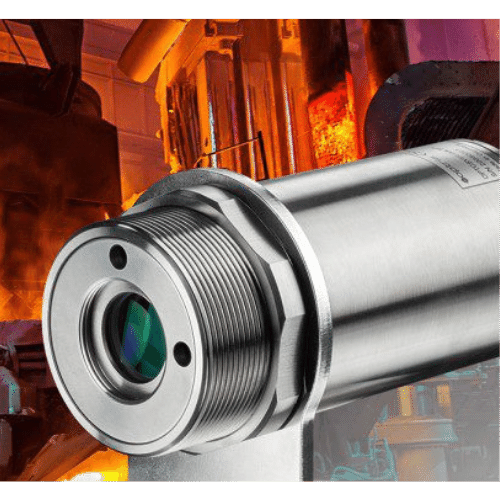
IR Pyrometers
IR (Infrared) pyrometers are non-contact temperature measurement instruments that utilize infrared radiation to determine the surface temperature of an object. They operate by emitting and receiving infrared radiation, which is then analyzed to calculate the temperature of the object. IR pyrometers are commonly used in various industries such as steel, glass, and ceramics manufacturing, as well as in research and development applications, where precise and accurate temperature measurements are required. They offer several advantages over traditional contact thermometers, including faster response times, higher accuracy, and the ability to measure temperatures in harsh environments without physical contact.
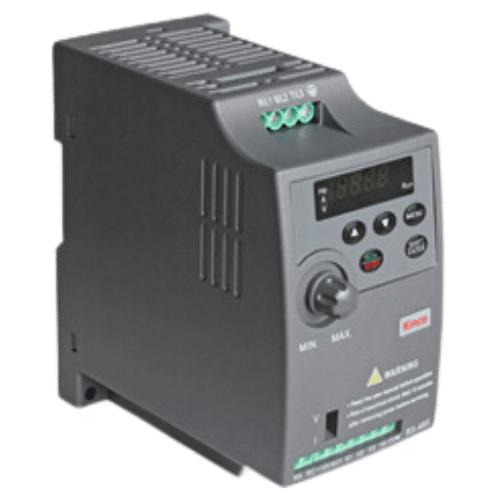

VFD (Variable Frequency Drive)
A VFD (Variable Frequency Drive) is an electrical device used to regulate the speed and torque of AC motors. It achieves this by varying the frequency and voltage supplied to the motor, allowing for precise control over its output. VFDs are commonly used in industrial applications such as pumps, fans, and conveyors to optimize energy efficiency, reduce maintenance costs, and improve overall system performance. They also provide soft starts and stops for motors, reducing wear and tear on equipment.
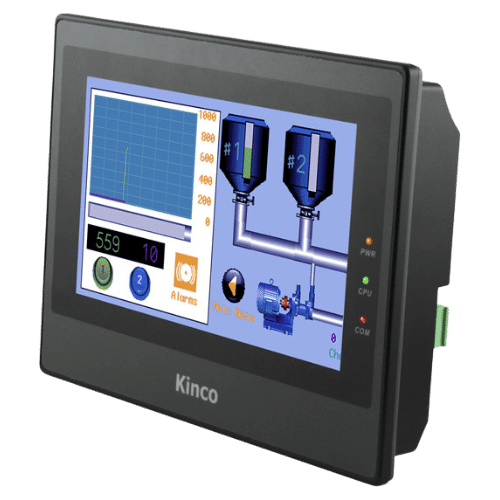

HMI (Human Machine Interface)
HMI, or Human Machine Interface, refers to the visual and interactive elements that allow operators to interact with and monitor industrial equipment and processes. It typically includes displays, buttons, switches, and other input/output devices that enable real-time data acquisition, analysis, and control. HMI systems are designed to improve efficiency, safety, and productivity by providing clear and intuitive operator interfaces that facilitate decision-making and troubleshooting. They also enable remote monitoring and diagnostics, reducing maintenance costs and downtime. Overall, HMI technology plays a critical role in the modernization of industrial automation and the Internet of Things (IoT).
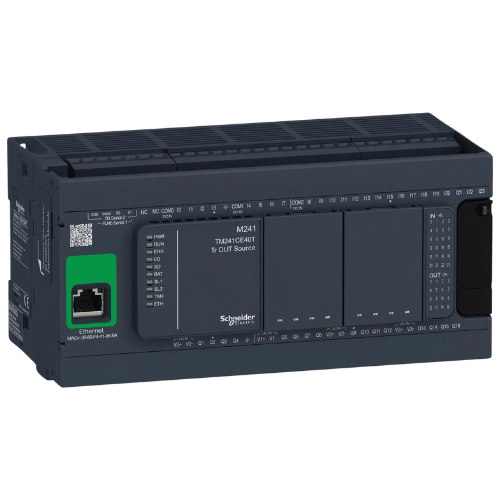

PLC (Programmable logic Controllers)
PLC (Programmable Logic Controllers) are digital devices used to control and automate various industrial processes. They consist of a central processing unit, input/output modules, and memory to store programs. PLCs can be programmed using a variety of languages, such as ladder logic, structured text, or instruction list, to perform complex logic operations and sequences. They offer advantages such as flexibility, ease of programming, and reliability, making them a popular choice in industries like manufacturing, automotive, and packaging.

Industrial POE & Network Switches
Our range of industrial POE (Power over Ethernet) and network switches are designed to meet the demands of harsh environments. These switches offer reliable connectivity, enabling seamless communication between devices in industrial settings. The POE functionality eliminates the need for separate power sources, reducing clutter and simplifying installation. Our switches are built with robust components, ensuring durability and reliability in extreme temperatures, vibrations, and electromagnetic interference. Additionally, they offer advanced features such as VLAN, QoS, and SNMP management for enhanced network control and monitoring.
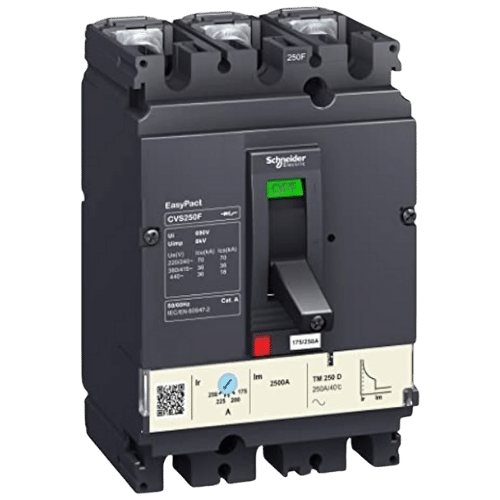

Switchgears
Switchgears are essential components in electrical power systems that provide protection, control, and management of electrical circuits. They are designed to safely and quickly isolate faults, disconnect equipment, and reroute power to maintain system reliability and prevent damage to equipment. Switchgears can be found in various applications, such as power generation, transmission, and distribution systems, as well as in industrial and commercial settings. They come in different types, including air-break, oil-break, and gas-break switchgears, and can be operated manually or automatically using digital or analog control systems.
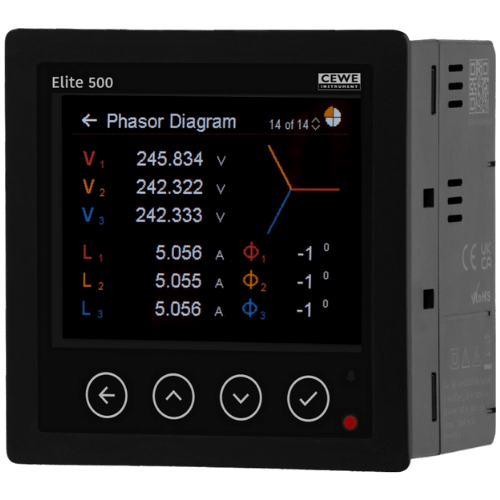

Multi Function Meter
A Multi Function Meter, also known as a Multimeter, is a versatile testing instrument that combines the functionality of several individual meters into a single device. It allows for the measurement of various electrical parameters such as voltage, current, resistance, and continuity, making it a valuable tool for diagnosing and troubleshooting electrical issues in various applications, including electronics, automotive, and industrial settings. Its compact size and user-friendly interface make it a convenient and practical choice for both professionals and hobbyists alike.
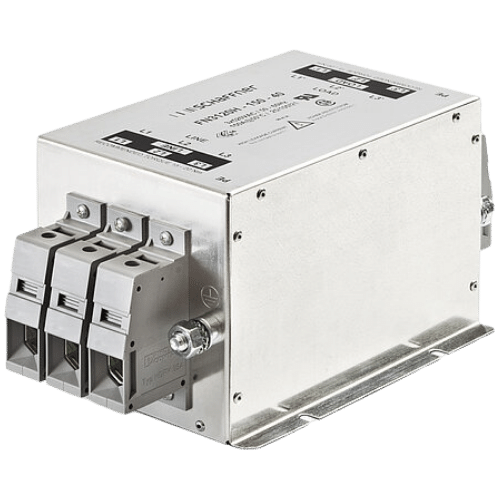
Schaffner Harmonics Filter
The Schaffner Harmonics Filter is a type of power quality conditioner designed to mitigate the negative effects of harmonics on electrical systems. Harmonics are high-frequency components that are generated by non-linear loads such as electronic equipment, variable frequency drives (VFDs), and welding machines. These harmonics can cause distortion in the electrical waveform, leading to increased energy consumption, overheating of equipment, and reduced lifespan of electrical components. The Schaffner Harmonics Filter uses a combination of passive and active filtering techniques to reduce harmonic distortion and improve power factor. Passive filters use capacitors and inductors to block or absorb harmonic frequencies, while active filters use power electronics to generate a compensating waveform that cancels out the harmonic content.
